EMG vs. NCS: What’s the Difference and When Are They Needed?
EMG vs. NCS: What’s the Difference and When Are They Needed?
Electromyography (EMG) and Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS) are essential diagnostic tools used to evaluate the health and function of muscles and nerves. While they are often performed together, these tests serve distinct purposes and provide complementary information. If you’re experiencing muscle weakness, numbness, or other symptoms affecting your muscles or nerves, understanding the difference between EMG and NCS can help you prepare for your diagnostic journey.
What Is EMG?
Electromyography (EMG) is a test that measures the electrical activity of muscles at rest and during contraction. By inserting a thin needle electrode into specific muscles, EMG can detect abnormalities in muscle function.
What Does EMG Assess?
EMG evaluates the communication between your nerves and muscles, helping neurologists identify:
- Muscle diseases (e.g., muscular dystrophy).
- Neuromuscular junction disorders (e.g., myasthenia gravis).
- Nerve damage (e.g., radiculopathy from a pinched nerve).
When Is EMG Needed?
Your doctor might recommend EMG if you experience:
- Persistent muscle weakness.
- Muscle cramps or twitching.
- Difficulty moving certain muscles.
What Is NCS?
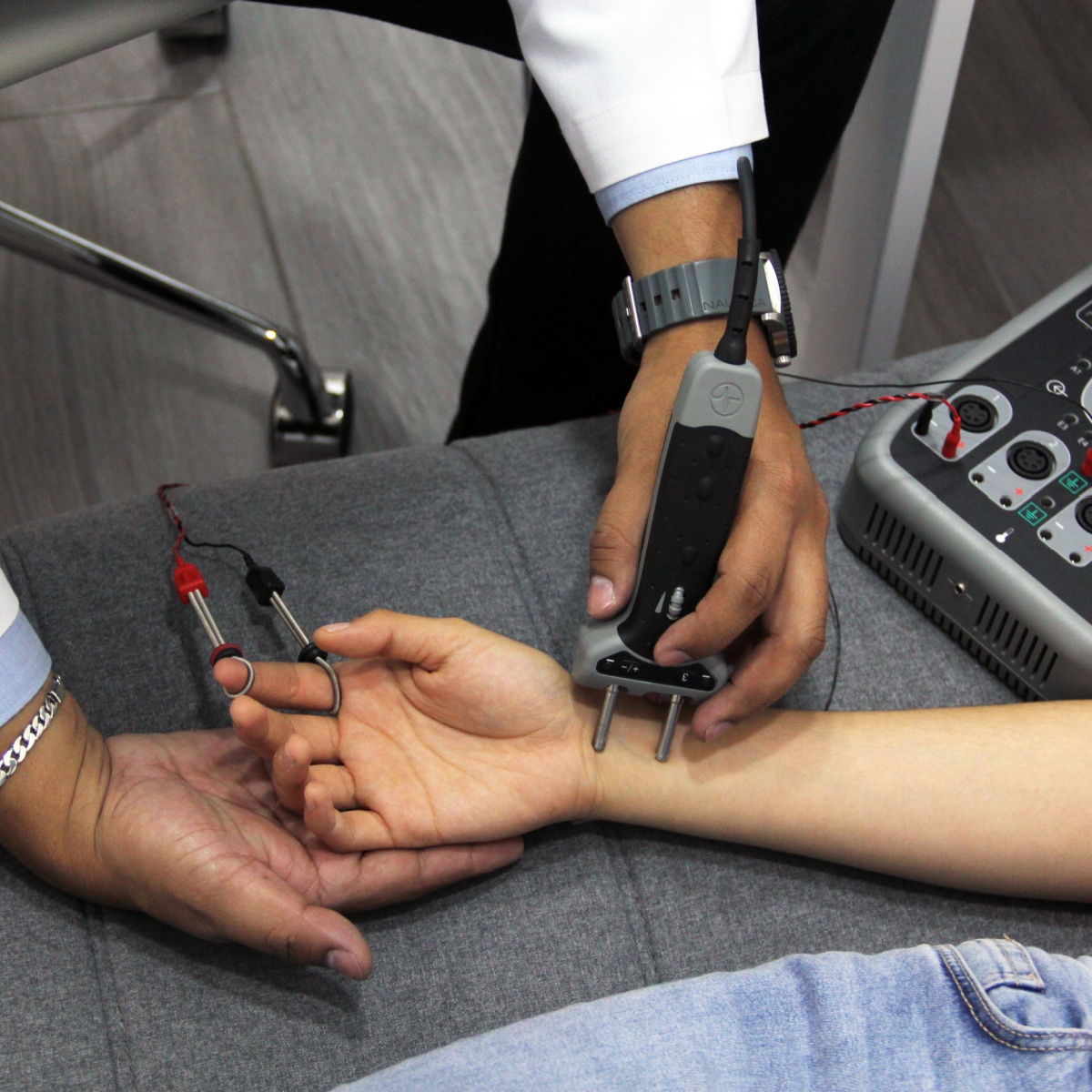
Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS) measure how well electrical signals travel through your peripheral nerves. During the test, electrodes are placed on the skin to stimulate a nerve, and the response is recorded.
What Does NCS Assess?
NCS focuses on nerve function and helps diagnose:
- Peripheral neuropathy (e.g., caused by diabetes or toxins).
- Carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Nerve compression or damage.
When Is NCS Needed?
Your doctor might recommend NCS if you have:
- Tingling or numbness in your hands, feet, or limbs.
- Nerve pain or sensitivity.
- Muscle weakness or reduced coordination.
| Feature | EMG | NCS |
| Purpose | Evaluate muscle electrical activity | Measures nerve signal transmission |
| Procedure | Needle electrode inserted into the muscle | Surface electrodes placed on the skin |
| Focus | Muscle and nerve communication | Nerve function |
| Common Use Cases | Muscle diseases, radiculopathy | Neuropathy, carpel tunnel syndrome |
| Discomfort Level | Mild discomfort from needle insertion | Minimal discomfort during stimulation |
While EMG directly examines muscle health, NCS evaluates how efficiently nerves transmit signals. Together, they offer a comprehensive view of neuromuscular health.
When Are EMG and NCS Performed Together?
EMG and NCS are often used together to:
- Differentiate Between Nerve and Muscle Issues: If a patient has a weakness, these tests can determine whether the problem originates in the nerves, muscles, or the communication between them.
- Confirm a Diagnosis: For conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome, the combined results of EMG and NCS provide a more accurate diagnosis.
- Plan Treatment: These tests guide neurologists in tailoring effective treatment plans, such as physical therapy, medication, or surgery.
Conditions Diagnosed with EMG and NCS
These tests are instrumental in diagnosing a variety of conditions, including:
- Peripheral Neuropathy: Often caused by diabetes or injuries, it leads to tingling, numbness, or pain in the extremities.
- Radiculopathy: Pinched nerves in the spine causing pain or weakness in the arms or legs.
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Compression of the median nerve in the wrist leading to hand weakness and tingling.
- ALS (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis): A progressive neurological disease affecting motor neurons.
- Muscle Disorders: Conditions like muscular dystrophy or polymyositis.
What to Expect During EMG and NCS
Both tests are performed in an outpatient setting and typically take 30–90 minutes, depending on the complexity.
EMG Procedure
- A thin needle electrode is inserted into specific muscles.
- The patient may be asked to contract the muscle to measure its activity.
- Some mild discomfort may occur during needle insertion.
NCS Procedure
- Surface electrodes are placed on the skin over the nerve being tested.
- A small electrical impulse stimulates the nerve.
- Patients may feel a mild tingling or twitching sensation.
Both tests are safe, and any discomfort is usually brief and manageable.
How HNNC Provides EMG and NCS Services
At Hashwani Neurology & Neurophysiology Clinic (HNNC), we specialize in state-of-the-art diagnostic techniques, including EMG and NCS, to evaluate and treat a wide range of neurological and neuromuscular conditions. Our team of experienced neurologists ensures a thorough and accurate diagnosis to guide your treatment.
We use EMG and NCS to diagnose conditions like:
- Carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Neuropathy.
- Muscle disorders.
- Spinal nerve issues.
With advanced equipment and a patient-centered approach, we ensure your diagnostic experience is as comfortable and effective as possible.
Contact HNNC for EMG and NCS Testing
If you’re experiencing symptoms like muscle weakness, numbness, or nerve pain, the Hashwani Neurology & Neurophysiology Clinic (HNNC) is here to help. Our expert team is dedicated to providing comprehensive care to improve your quality of life.
Contact us today to schedule a consultation and learn more about how EMG and NCS testing can help diagnose and treat your condition.