Deep Brain Stimulation: How It Works and Who Can Benefit
Deep Brain Stimulation: How It Works and Who Can Benefit
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) is a revolutionary therapy that has transformed the lives of individuals with neurological disorders. By delivering targeted electrical impulses to specific areas of the brain, DBS helps manage symptoms and improve quality of life when other treatments fall short. But how does it work, and who is it best suited for? This blog explores everything you need to know about DBS and its potential benefits.
What Is Deep Brain Stimulation?
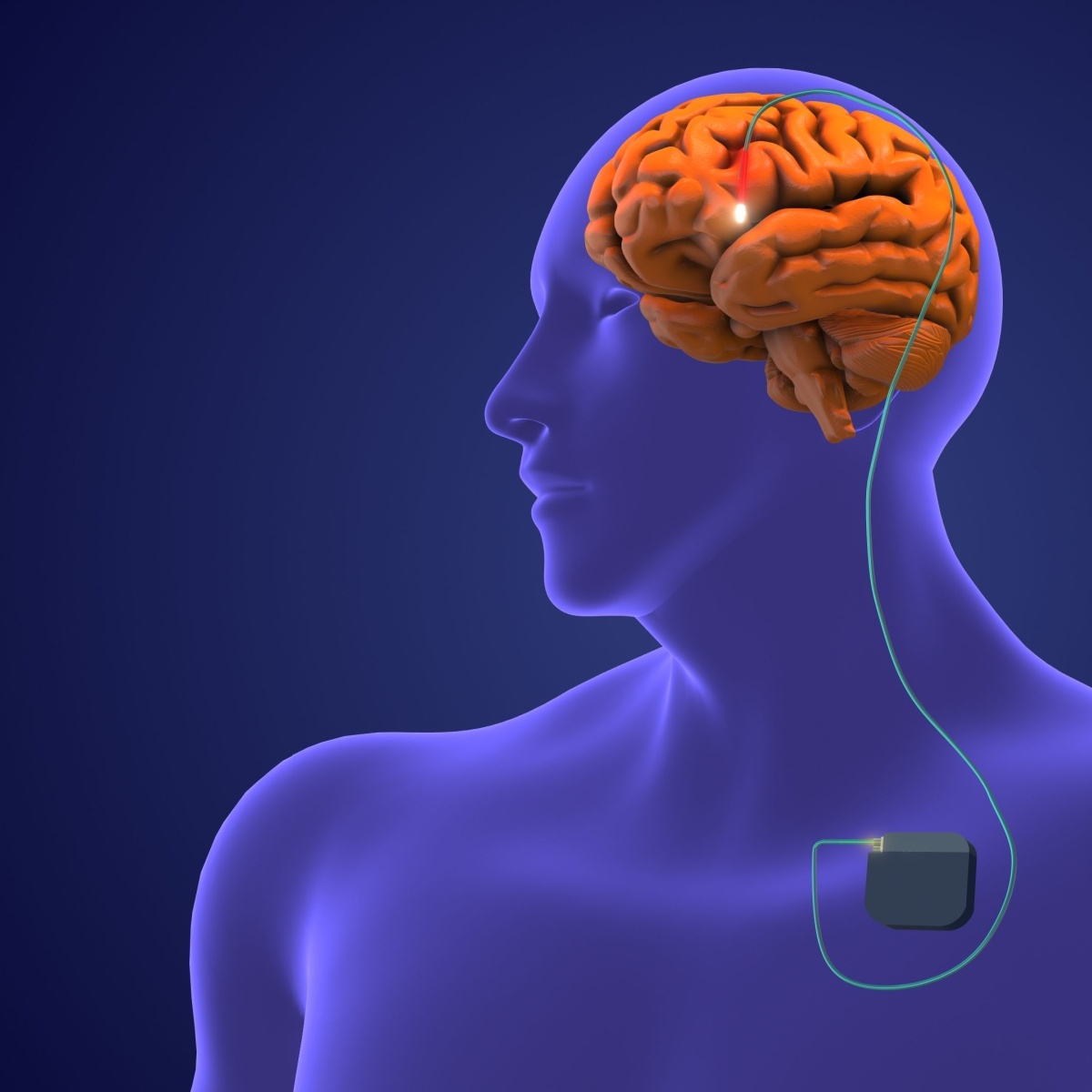
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) is a surgical procedure used to treat neurological conditions by implanting electrodes in specific areas of the brain. These electrodes are connected to a small, pacemaker-like device implanted in the chest, known as a neurostimulator. The device sends controlled electrical impulses to the brain, disrupting abnormal signals that cause symptoms in various disorders.
DBS does not cure neurological conditions, but it helps manage symptoms that significantly affect daily life, offering patients better control over their health.
How Does DBS Work?
DBS works by targeting precise regions of the brain responsible for specific symptoms. The process includes the following steps:
- Surgical Implantation:
Electrodes are placed in the targeted brain area, such as the thalamus, subthalamic nucleus, or globus pallidus, depending on the condition being treated.
A neurostimulator is implanted under the skin of the chest. - Programming the Device:
After the procedure, the neurostimulator is programmed to deliver customized electrical impulses to manage symptoms effectively. The settings can be adjusted over time based on patient needs. - Ongoing Monitoring:
Neurologists monitor the device’s effectiveness and make adjustments as necessary.
The electrical impulses modify abnormal brain activity without causing permanent damage to the brain. This makes DBS a versatile and adjustable treatment option.
Who Can Benefit from Deep Brain Stimulation?
DBS is most commonly used to treat movement disorders and other neurological conditions. Here are some conditions where DBS has shown significant benefits:
1. Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurological disorder that affects movement. DBS is most often recommended for patients with advanced Parkinson’s who experience severe motor symptoms that are not adequately controlled with medication.
DBS is particularly effective in managing:
Tremors: Involuntary shaking that can interfere with tasks like holding a glass or writing.
Rigidity: Muscle stiffness that makes movement difficult or painful.
Bradykinesia: Slowness of movement, a hallmark of Parkinson’s.
Dyskinesias: Involuntary, erratic movements often caused by long-term use of Parkinson’s medications like levodopa.
DBS can also help reduce the dependency on high doses of medication, minimizing the risk of side effects such as nausea, dizziness, and hallucinations. This allows patients to regain more control over their daily lives.
2. Essential Tremor
Essential tremor is one of the most common movement disorders, characterized by uncontrollable shaking, typically in the hands or arms. It can make everyday activities like eating, writing, or drinking from a cup nearly impossible.
DBS provides significant relief for patients with essential tremor by:
- Reducing the severity of tremors.
- Restoring the ability to perform fine motor tasks.
- Improving social confidence for individuals who may feel self-conscious about their condition.
Patients with essential tremor who do not respond to medications like beta-blockers or anticonvulsants are often ideal candidates for DBS.
3. Dystonia
Dystonia is a neurological disorder that causes sustained or repetitive muscle contractions, leading to abnormal postures or movements. Severe cases of dystonia can be debilitating, causing pain and significantly limiting mobility.
DBS can be highly effective for:
- Reducing involuntary muscle contractions.
- Improving posture and movement patterns.
- Enhancing quality of life by allowing patients to engage in daily activities with less discomfort.
In particular, patients with generalized dystonia or segmental dystonia (affecting multiple areas of the body) may see dramatic improvements with DBS.
4. Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a condition characterized by recurrent seizures due to abnormal electrical activity in the brain. While medications can control seizures in many patients, about one-third of individuals with epilepsy are considered drug-resistant, meaning their seizures persist despite treatment.
DBS offers a promising option for these patients by:
- Reducing the frequency and severity of seizures.
- Improving overall seizure management when other treatments, including vagus nerve stimulation or resective surgery, are not effective or appropriate.
- Enhancing quality of life by minimizing the unpredictability of seizures.
DBS for epilepsy targets areas of the brain, like the anterior nucleus of the thalamus, which plays a role in seizure activity.
Benefits of Deep Brain Stimulation
DBS offers several advantages for patients with treatment-resistant neurological disorders:
- Improved Symptom Control:
DBS significantly reduces symptoms that interfere with daily life, such as tremors, stiffness, and seizures.
- Adjustable and Reversible:
Unlike other surgical options, DBS is adjustable and can be fine-tuned as the patient’s condition changes. It is also reversible if needed.
- Reduced Medication Dependency:
Many patients experience a reduction in medication dosage and associated side effects.
- Enhanced Quality of Life:
With better symptom control, patients can regain independence and participate in daily activities more effectively.
Are There Risks to DBS?
As with any surgical procedure, DBS carries potential risks, including:
- Infection at the surgical site.
- Bleeding or swelling in the brain.
- Temporary side effects, such as headaches, speech problems, or mood changes.
However, serious complications are rare, and the procedure is generally well-tolerated. Patients considering DBS should discuss the risks and benefits with their neurologist to make an informed decision.
Is DBS Right for You?
DBS is typically recommended for patients who:
- Have not responded well to medications or other treatments.
- Experience significant disruption in their daily lives due to their symptoms.
- Are in good overall health and can tolerate the surgical procedure.
A thorough evaluation by a neurologist or neurosurgeon is necessary to determine whether DBS is a suitable option.
How Hashwani Neurology & Neurophysiology Clinic (HNNC) Can Help
At Hashwani Neurology & Neurophysiology Clinic (HNNC), we specialize in advanced neurological diagnostics and treatments, including Deep Brain Stimulation. Our experienced team of neurologists works closely with patients to determine the best course of treatment based on their unique needs and conditions. From initial evaluations to ongoing DBS programming, we are committed to improving our patients’ quality of life.
Contact HNNC to Learn More About DBS
If you or a loved one is considering Deep Brain Stimulation or seeking treatment for a neurological condition, the Hashwani Neurology & Neurophysiology Clinic (HNNC) is here to help. Our team is dedicated to providing compassionate, cutting-edge care for a wide range of neurological disorders. Contact us today to learn more about our services.
Dr. Hashwani is here to guide you every step of the way. Schedule an appointment and take the first step toward better neurological health.